Nepal Forest Cover Analysis 1984 to 2022
1. Introduction
As I stroll along the familiar path today, I find myself amidst a lively conversation among forestry students discussing the intriguing topic of Nepal’s forest cover analysis. Some voices resonate with optimism, claiming that Nepal’s forest cover is on the rise, while others seek tangible evidence to support this claim. Intrigued by their discussions, I couldn’t help but ponder how this significant Nepal Forest Cover Analysis 1984 to 2022 transformation could be visually represented.
2. Prompting Reflections on Fluctuating Patterns
Back in my office, the thought lingers, and I contemplate the implications of the fluctuating patterns in Nepal’s forest cover analysis. My experience spanning a decade in utilizing GIS and Remote Sensing techniques to analyze land areas across the globe prompts me to explore this challenge. However, my initial search for precise data on Nepal’s forest cover analysis proves futile, as existing platforms fail to provide comprehensive information on forest cover areas.
3. Embarking on a GIS and Remote Sensing Quest
Driven by curiosity and determination, I embark on a quest to leverage GIS and Remote Sensing technology to map Nepal forest cover analysis 1984 to 2022. The journey begins with navigating through various websites, scouring for the elusive data. It’s a thrilling suspense, and I am eager to share insights with those keen on unraveling this intricate process.
4. Unveiling the Evolution of Nepal’s Forest Cover
After overcoming initial hurdles and employing Geo-processing tools, I successfully calculate the Nepal forest cover area for 1984 to 2022, marking the beginning of a detailed Nepal Forest Cover Analysis. Yet, the quest for comprehensive data persists, leading me to discover a treasure trove of time-series data that unveils Nepal forest cover analysis 1984 to 2022 evolution over the years. Through meticulous geo-spatial and temporal analyses, the data reveals intriguing patterns. From 1984 to 2022, the forest cover area undergoes fluctuations, presenting a nuanced narrative of environmental changes. These insights not only inform but also inspire further exploration and understanding of Nepal’s ecological landscape.
5. Comparative Analysis of Forest Cover Data
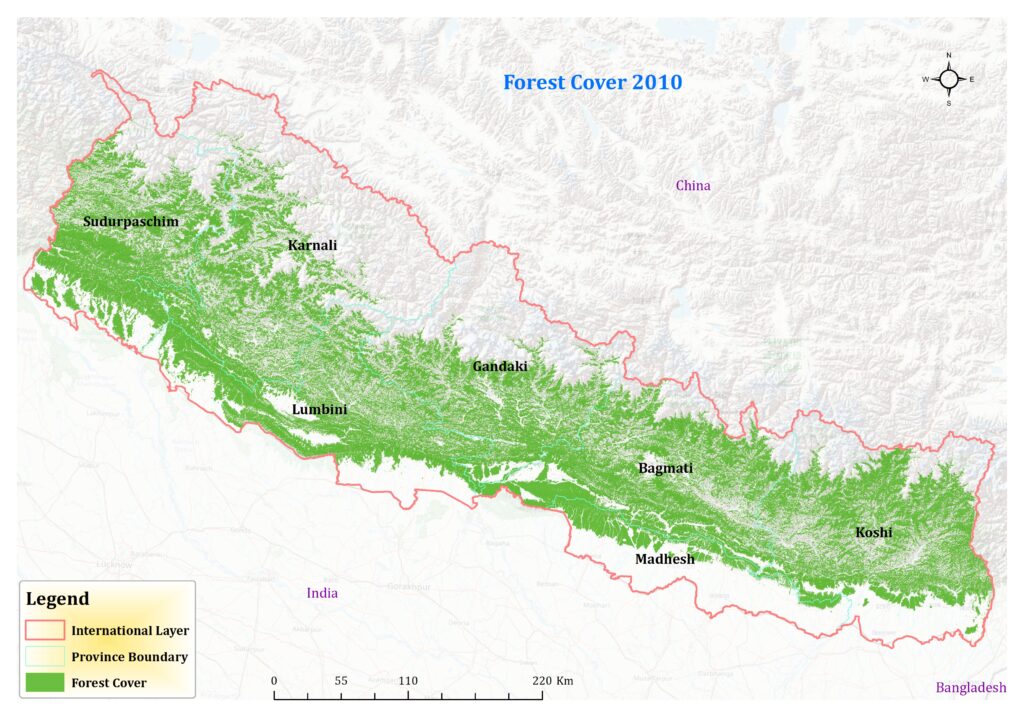
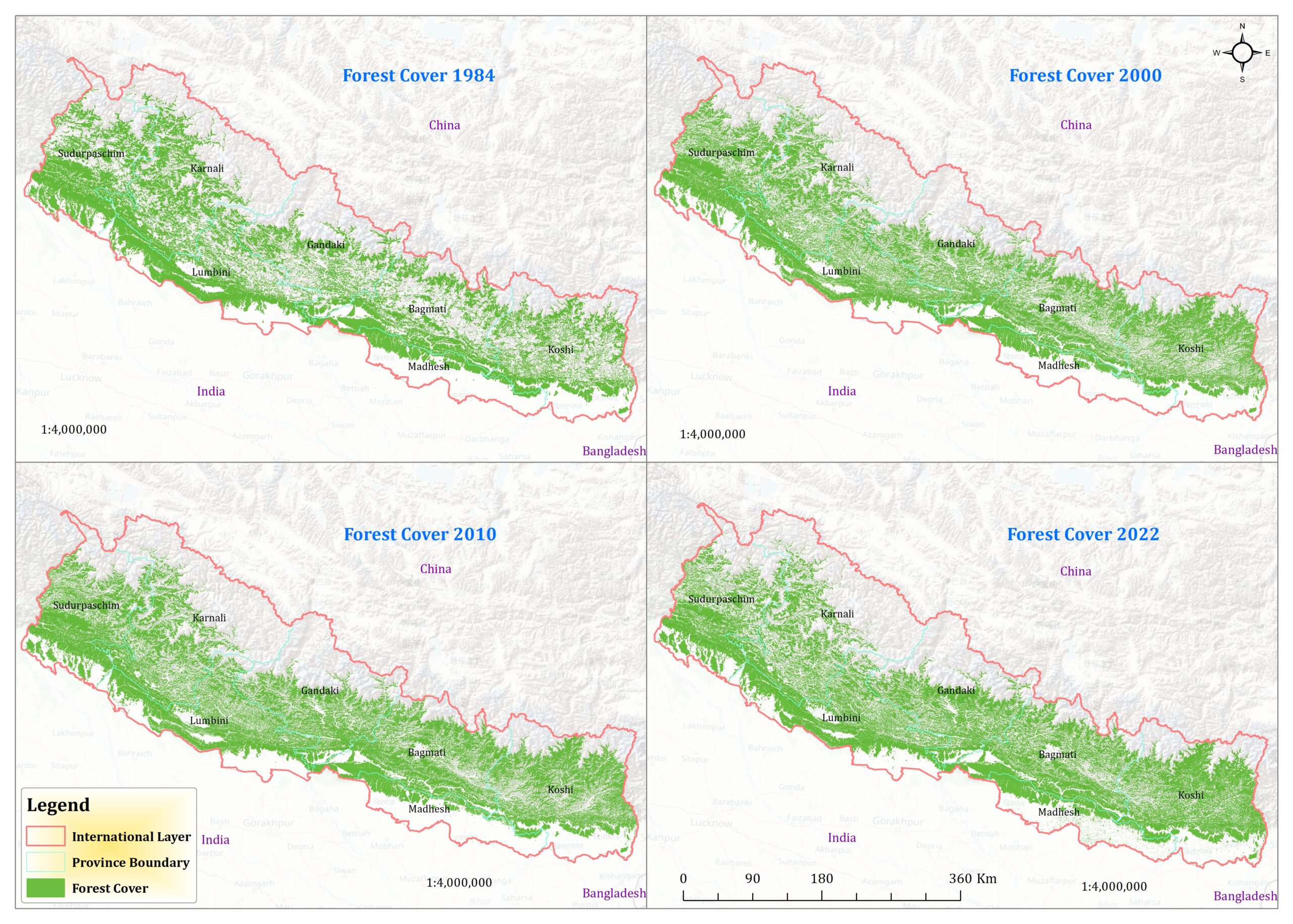
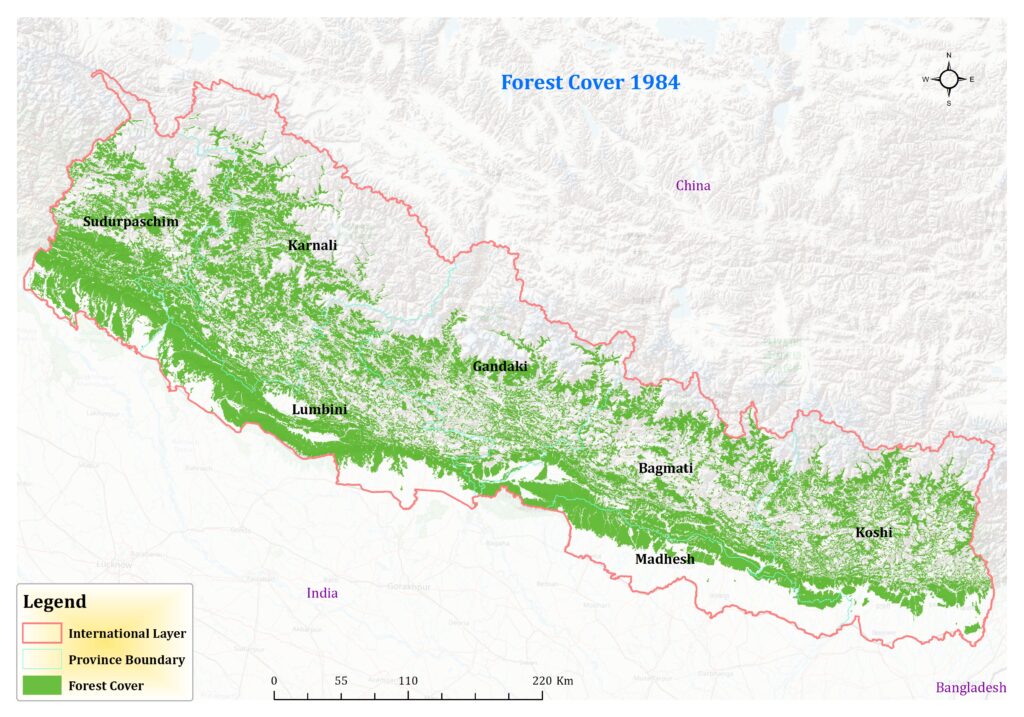
Certainly, let’s delve into a comparative analysis of the forest cover data for Nepal across different years: 1984, 2000, 2010, and 2022. The data provides a fascinating insight into the evolution of Nepal’s forest cover analysis over nearly four decades. In 1984, the forest cover stood at 56,290 square kilometers. This baseline measurement serves as a crucial starting point for understanding the subsequent changes in forest cover. Moving forward to the year 2000, we observe a notable increase in Nepal forest cover analysis 1984 to 2022, reaching 59,155 square kilometers.
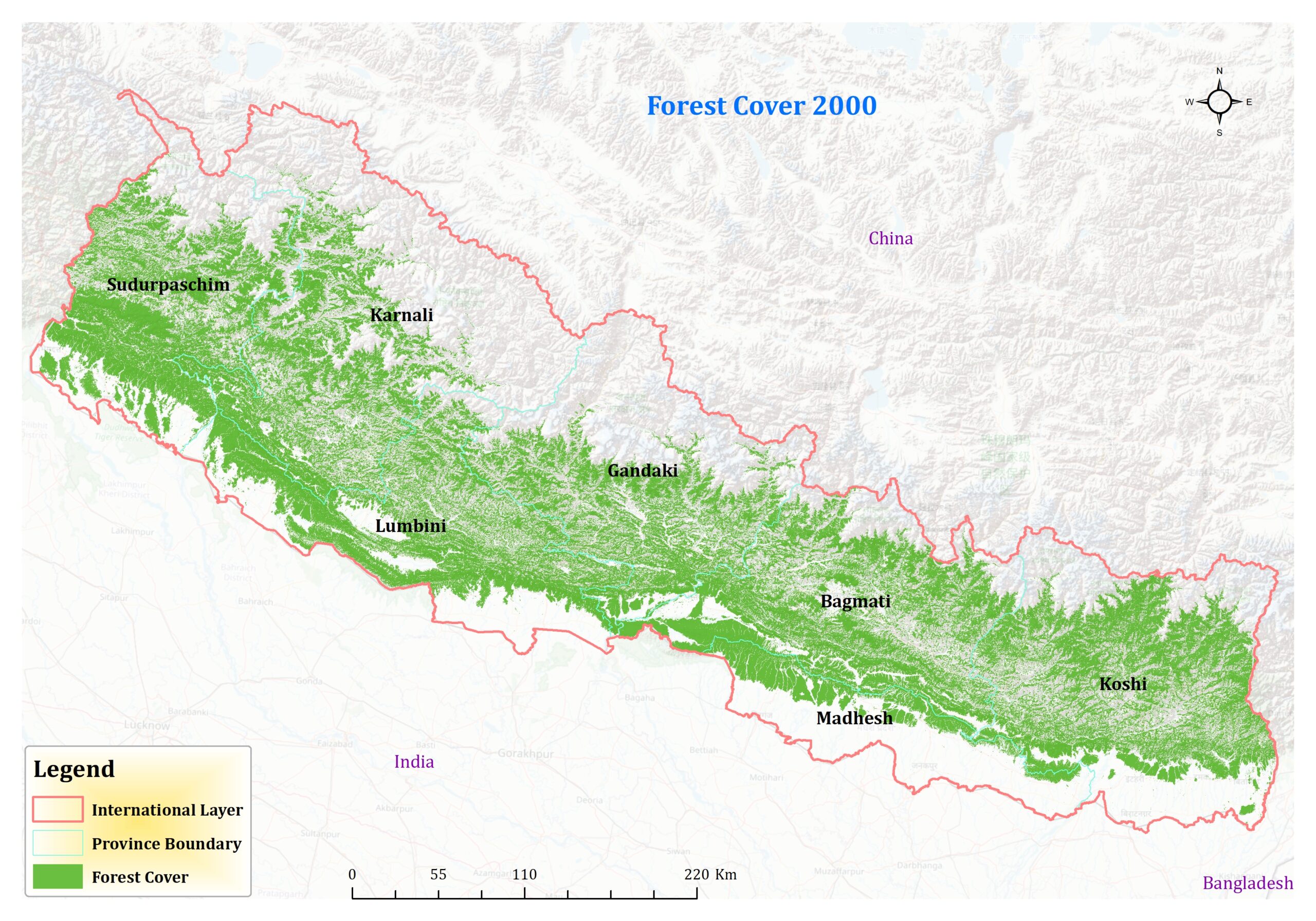
This uptick suggests positive trends in forest conservation efforts or natural regeneration processes occurring within this period. The increase of approximately 2,865 square kilometers over 16 years reflects a steady growth in forested areas. The most significant leap in forest cover analysis is observed between 2000 and 2010, where the forested area expands to 69,311 square kilometers. This substantial increase of over 10,000 square kilometers within a decade signifies substantial strides in forest conservation and reforestation initiatives. It reflects concerted efforts by stakeholders to protect and restore forest ecosystems, likely driven by environmental policies and community-driven conservation projects.
However, the data takes a slight downturn by the year 2022, with the forest cover analysis decreasing to 62,688 square kilometers. While the overall trend still shows an increase compared to the baseline in 1984, this decline highlights potential challenges or factors impacting forest conservation efforts in recent years. Factors such as deforestation due to urbanization, agricultural expansion, or natural disturbances like wildfires could contribute to this decline.
6. Insights and Implications
It’s essential to conduct further analysis to understand the drivers behind these fluctuations and devise targeted strategies for sustainable forest cover analysis management. Geographic information systems (GIS) and remote sensing technologies play a vital role in monitoring and analyzing such trends, providing valuable insights for informed decision-making and conservation planning.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, the comparative analysis of Nepal forest cover analysis 1984 to 2022 data for Nepal unveils a dynamic narrative of environmental changes over time. While there have been periods of substantial growth, challenges and fluctuations also underscore the ongoing need for proactive conservation measures to safeguard Nepal’s rich biodiversity and ecosystem services for future generations.