Introduction to Nepal India Regional Trade and Transport Project (NIRTTP)
In 2017, the Nepal-India Regional Trade and Transport Project (NIRTTP) was a milestone in regional collaboration. Funded by the World Bank, it enhanced trade and transport between Nepal and India, focusing on Chitwan/Parsa NPs’ Road Safety Challenges and Human Wildlife Conflict (HWC) – 2017. The project upgraded transportation corridors, improved border infrastructure, and optimized customs facilities. NIRTTP strategically addressed road safety and wildlife collisions, fostering safer regional trade. By eliminating bottlenecks and embracing modern practices, it significantly reinforced economic bonds, laying the groundwork for a seamless cross-border transportation network. This initiative played a crucial role in bolstering economic growth and connectivity in South Asia, marking a pivotal moment in the region’s infrastructure development.
To Address Human Wildlife Conflict by Using GIS in NIRTTP: Enhancing Project Effectiveness
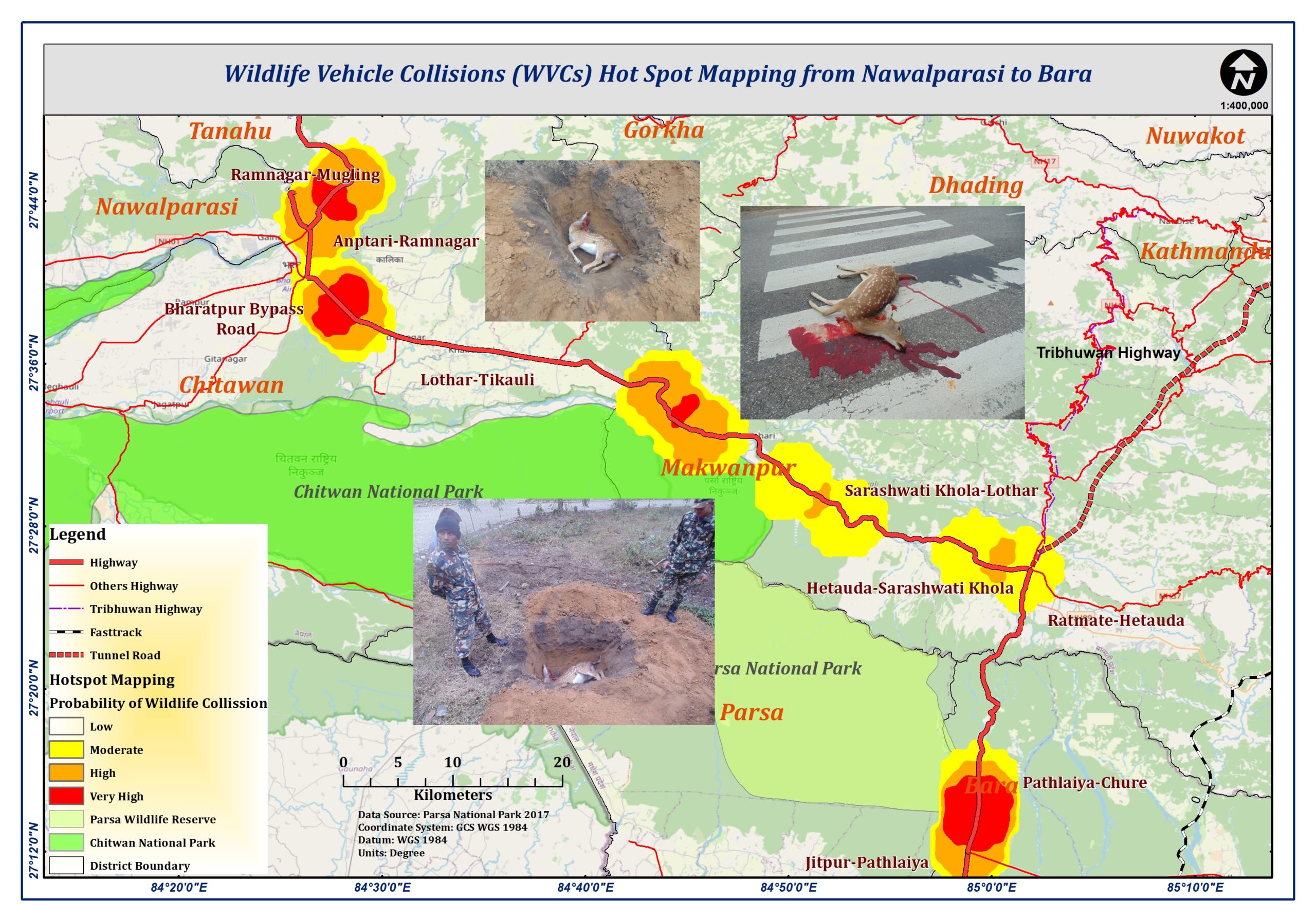
As the GIS expert at NIRTTP, my pivotal role significantly contributed to enhancing the project’s efficacy, specifically addressing “Road Safety Challenges and understanding Human Wildlife Conflict (HWC) in Chitwan/Parsa NPs.” Utilizing Geographic Information System (GIS) technology, I mapped essential elements like transportation corridors, border infrastructure, and wildlife habitats along vital routes such as Aanptari-Ramnagar, Bharatpur Bypass Road, and Pathlaiya-Chure highway. My duties included pinpointing potential wildlife-vehicle collision hotspots, suggesting strategic wildlife crossing locations, and visualizing data for informed decision-making. Integrating geospatial information played a vital role in optimizing route planning, minimizing environmental impact, and supporting the project’s overarching goals of improving regional trade, transport connectivity, and addressing road safety challenges and wildlife collisions.
Assessment of Wildlife Vehicle Collisions: Factors and Probability
To assess the likelihood of Human Wildlife Conflict (HWC) in Chitwan/Parsa NPs along designated highways, a thorough analysis of contributing factors is essential. High-risk areas exhibit characteristics like dense wildlife populations, movement patterns, and crossing points intersecting with roads. In the Chitwan and Parsa National Parks region, the Aanptari-Ramnagar and Bharatpur Bypass Road pose a significant risk of wildlife vehicle collisions, being near conservation areas renowned for diverse fauna. Incident probability may gradually decrease from very high to low, influenced by factors like wildlife density reduction, wildlife corridor implementation, and targeted conservation efforts in specific zones. This nuanced assessment forms the basis for developing effective strategies to mitigate road safety challenges and enhance understanding of wildlife collisions in these critical regions.
Mitigation Strategies for Wildlife-Vehicle Collisions
Effectively addressing Human Wildlife Conflict (HWC) in Chitwan/Parsa NPs requires a comprehensive strategy, integrating engineering, education, and enforcement measures. A crucial aspect involves strategically implementing wildlife crossings on critical routes like Aanptari-Ramnagar, Bharatpur Bypass Road, and Pathlaiya-Chure highway, providing safe passages for wildlife and reducing collision risks. Installing wildlife warning signs and implementing speed reduction measures in high-risk zones are essential to alert drivers about potential animal presence. Collaboration between wildlife conservation authorities, transportation agencies, and community groups is vital for public education on exercising caution in these areas. Regular monitoring and data collection on collision incidents are essential components, refining approaches and assessing the overall effectiveness of implemented measures in addressing road safety challenges and understanding wildlife collisions.
Recommendations and Future Steps
Collaborative efforts with local wildlife conservation authorities and transportation agencies are crucial next steps in addressing “Road Safety Challenges and understanding Wildlife Collisions.” Raising awareness about the extensive impact of collisions on both human and animal populations is imperative, highlighting the need for public education and community involvement. Establishing a framework for regular monitoring, data collection, and strategy refinement is essential for developing sustainable solutions that balance transportation needs with wildlife conservation efforts. As the Nepal India Regional Trade and Transport Project (NIRTTP) continues to facilitate trade and transport between Nepal and India, integrating these strategies will further enhance road safety and promote wildlife conservation in the region.